Artificial intelligence is rapidly impacting health care, powering medical devices that can diagnose conditions and monitor patients in real time. However, along with these promising benefits come risks unique to these new gadgets and networks. Technicians and health care organizations must understand these four common challenges and prioritize security for patients and staff.
1. Protecting Sensitive Patient Data
AI-enabled medical devices rely heavily on patient data to function effectively. They collect, process and sometimes transmit large amounts of sensitive patient information, including medical histories and real-time biometrics. This wealth of information makes them attractive targets for cybercriminals. IBM researchers have found that 97% of organizations have already encountered AI-related security incidents and lack the proper safeguards.
Health care data breaches can have severe consequences. Aside from financial loss and operational issues, exposing patient data can erode trust in medical and tech institutions, and possibly lead to legal consequences.
2. The “Black Box” Problem and Algorithmic Bias
AI models have come a long way in health care, detecting conditions like skin cancer or diabetic retinopathy with 95% and 90% accuracy, respectively. However, many of these models operate as “black boxes,” meaning their internal processes can be difficult to understand. From a cybersecurity perspective, this lack of transparency may conceal vulnerabilities or malicious algorithms.
If an attacker alters the training data or other components of the model, the device may appear to function normally while producing inaccurate or biased results. In medical settings, these inconsistencies can directly affect patients’ health and safety. They can also raise ethical and compliance concerns, especially when AI performs differently across patient demographics.
3. Vulnerabilities in Connectivity and Integration
AI-powered medical devices often need to connect with hospital networks, electronic health records, cloud platforms or other devices. While these connections support functionality and convenience, each additional device or network introduces new vulnerabilities.
Wireless communication and remote monitoring are common entry points for attackers. If a hospital uses outdated software or hardware systems, it can further complicate this issue, as legacy systems may lack the necessary technology to protect against modern threats.
4. Evolving Regulatory and Compliance Landscapes
Since consumer-facing AI is a relatively new technology, regulatory requirements for these devices are still developing and can vary across regions. Companies need to comply with health care regulations and data protection laws while adapting to new, emerging rules.
This complexity can make it challenging for health care providers and cybersecurity specialists to stay compliant. Failing to meet these standards may lead to delayed approvals or legal penalties.
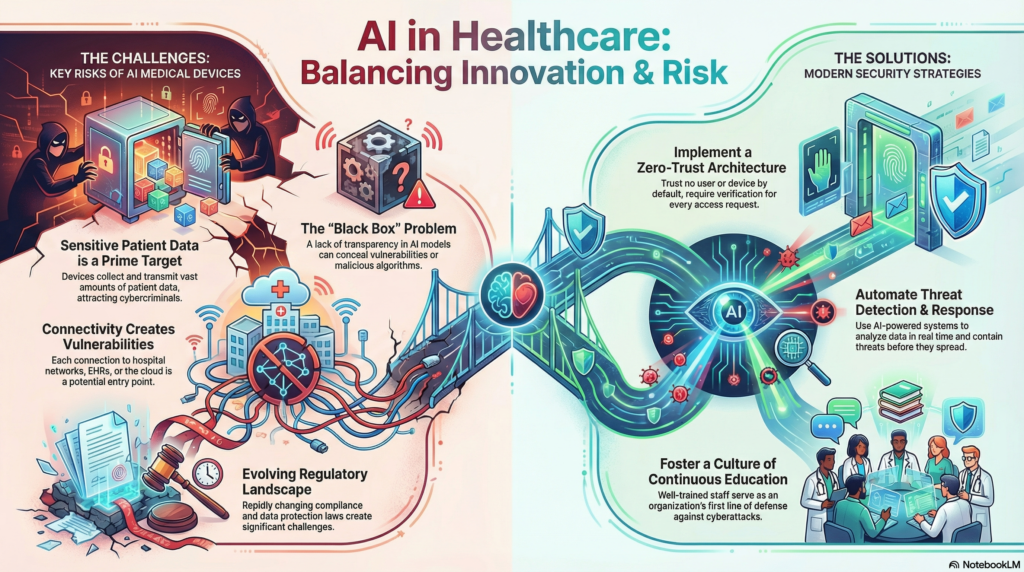
Modern Security Strategies to Overcome These Challenges
While using AI-enabled medical devices comes with significant challenges, health care organizations can minimize risk by adopting modern and strategic security practices.
Implement a Zero-Trust Architecture
Zero-trust security trusts no user or device by default, even those operating inside the network. Each access request will require verification before it can be processed. For AI medical devices, this approach limits the movement of potential attackers or malware, reducing the impact of compromised devices or accounts.
This security framework also enables better visibility. Since each access request needs authentication, the team can collect detailed logs that help security teams understand standard device or network activity and quickly spot suspicious behavior.
Automate Threat Detection and Response
Attackers are leveraging AI and automation to target and exploit their victims, with a 16.7% annual increase in the number of incidents. Security teams should leverage similar technologies to protect critical systems and infrastructure.
Automated threat detection systems can analyze large volumes of information in real time, identifying suspicious patterns that may come with malware or unauthorized access. This rapid response is critical in health care, as downtime or data manipulation can affect patient care. It can further reduce cybersecurity risks by containing threats before they spread or escalate.
Foster a Culture of Continuous Education
Human behavior and practices can be a common source of security incidents. Technicians and hospital staff should receive ongoing training on device security and cyber risks to ensure they are well-equipped to identify and report potential threats. Well-trained staff can be an organization’s first line of defense against cyberattacks.
From Awareness to Action
AI-enabled medical devices offer powerful capabilities, but they also bring new cybersecurity challenges that can put patients and staff at risk. Health care facilities and security teams must leverage technical controls with strong processes to maximize the benefits of AI while ensuring proper care and safety.
As the Features Editor at ReHack, Zac Amos writes about cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, and other tech topics. He is a frequent contributor to Brilliance Security Magazine.
.
.
Additional Resource
Video Overview
Follow Brilliance Security Magazine on LinkedIn to ensure you receive alerts for the most up-to-date security and cybersecurity news and information. BSM is cited as one of Feedspot’s top 10 cybersecurity magazines.


