Drones are versatile pieces of equipment for military operations and recreational activities, and have since gravitated toward commercial security applications. While drones are helpful for physical security, like monitoring the perimeter or providing an aerial view of the facility, these features are also beneficial toward cybersecurity. Teams can operate drones to enhance cybersecurity while also ensuring the drone’s system is safe from cyber threats.
Listen to the article
Ways to Use Drones Effectively for Cybersecurity
It can be challenging to imagine how physical drones can enhance cybersecurity, but the following are ways to leverage the capabilities of current drone designs to implement adequate cybersecurity measures.
Testing Physical Security with a Cyber Element
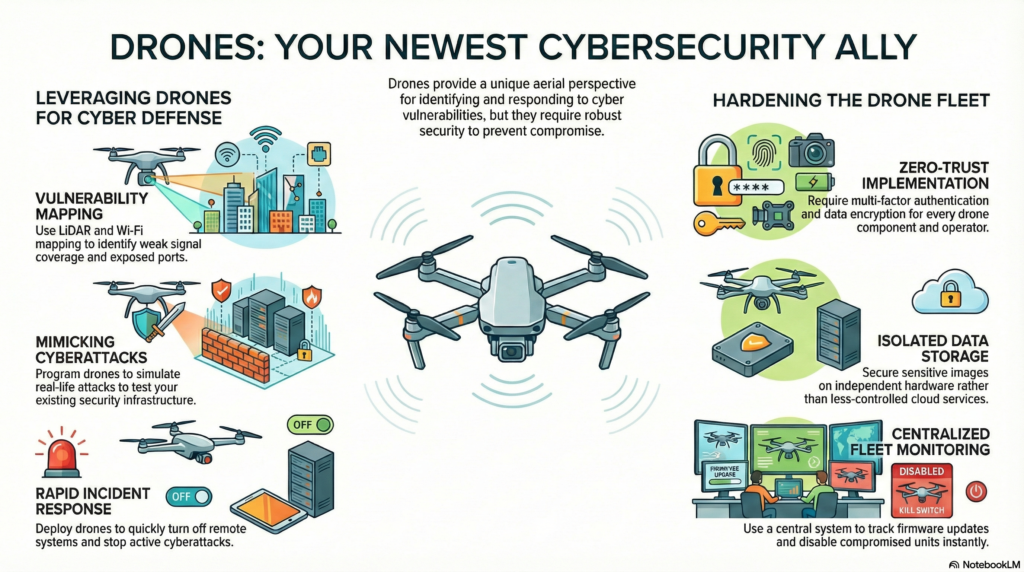
Teams can use drones to test physical security measures with a cyber element, such as control panels or security systems that are hard for humans to monitor. Some drones have a screen in their controllers, allowing operators to monitor the devices when out of sight. This allows teams to inspect otherwise out-of-sight antennas and satellites that transmit sensitive information, or spot exposed Ethernet ports on buildings. While these are physical security measures, the identified equipment includes valuable cybersecurity features.
Identifying Areas for Cybersecurity Equipment
Beyond identifying specific elements and checking for weaknesses, drones can provide a general aerial view of a facility as well. Cybersecurity teams can attach sensors to drones that create an accurate map of the building as it flies. If there are IoT sensors on a certain floor, a drone can detect them and transmit their exact location to personnel. Using additional features such as Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR), the drone’s map helps teams create more secure layout plans with cybersecurity in mind.
Responding to Incidents Quickly
Drone responses are much quicker than human responses. If team members can stop a cyberattack using a physical element, such as turning off a system or sending a signal to a remote device, drones can deploy quickly and achieve the goal. Once the attack ceases, cybersecurity teams can assess the damage and hopefully prevent future issues. The drone provides a quick fix so employees can begin improving the affected security measures.
Mimicking Cybersecurity Attacks
Some drone models can mimic real-life cybersecurity attacks to test current cybersecurity systems and identify potential weaknesses. For instance, cybersecurity teams can program a code into a drone and send the signal from the drone’s remote location, the same way a cyberattacker would incite an attack from an undisclosed area. Running a test like this alerts teams to weaknesses in their security systems, helping them protect against real hackers in the future.
Mapping Wi-Fi Networks
Drones can map Wi-Fi networks by flying over a facility and digitally detecting them. As it gathers the data, it creates a network map for cybersecurity teams to review. Using this map, teams can assess vulnerable network access points and identify weak signal coverages that attackers usually exploit.
Tips for Properly Securing Drones
Drones provide enhanced cybersecurity measures, such as those outlined above, but they are also vulnerable to cyberattacks. The following are ways cybersecurity teams can protect their drones against hackers.
Implement a Zero-Trust Policy
A zero-trust policy for drone cybersecurity treats every part of the drone as a potential attack surface. To address the concern, cybersecurity teams can implement systems to ensure each drone component is properly protected. Anyone who operates the drone must complete multiple authentication procedures, such as answering security questions or receiving a code, before using it.
Communication channels should have encryption, especially when transmitting data across networks. Hackers can infiltrate these networks and access sensitive data, especially when the drone is farther from the facility. Most encryption techniques use complex algorithms to shield data, preventing attackers from understanding it.
Information security is another prominent concern. Drones consistently collect sensitive images and record vulnerable information. Cybersecurity teams should secure data storage on a separate device from all other sources. Cloud services are not as safe as independent storage due to the larger attack surface and lack of control that comes with using the cloud.
Monitor Firmware and Software
The firmware and software on a drone must always be up to date with current technology. Cybersecurity teams should schedule regular checks to ensure they do not miss updates. Updates protect drones by equipping them with the latest firmware and software. Teams should also look for recalls to turn off their drones if necessary. Device recalls usually signal a significant flaw that could compromise cybersecurity if the device continues to be used.
Another tactic to protect firmware is to use a central system that controls the entire drone fleet. This kind of system makes it easier for cybersecurity teams to monitor all drones simultaneously and identify discrepancies early. If one drone is compromised, a team member can disable the entire system from a single location before the hacker can control them all.
Drones Are a Great Cybersecurity Measure
Drones are a great addition to cybersecurity measures, providing physical maps and identifying weaknesses from the sky. However, drones are still vulnerable to cyberattacks and must operate under proper security protocols to prevent cyberattackers from gaining access to their systems. Integrating drones into an existing cybersecurity team is a great strategy when implemented correctly.
As the Features Editor at ReHack, Zac Amos writes about cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, and other tech topics. He is a frequent contributor to Brilliance Security Magazine.
.
.
Additional Resource
Video Overview
Follow Brilliance Security Magazine on LinkedIn to ensure you receive alerts for the most up-to-date security and cybersecurity news and information. BSM is cited as one of Feedspot’s top 10 cybersecurity magazines.


